Baha-Bone Anchored Hearing Aid







HEARING AIDs STYLE IN ALL BRANDS WITH AFFORDABLE PRICE
Are you considering purchasing a hearing aid but are concerned about hearing aids style, its size, appearance, and suitability for you?
But don’t worry about the hearing aid type; our audiologist will assist you in making the right selection of hearing aids based on your budget and lifestyle and will provide a free trial in your setting. By boosting quiet noises, hearing aids unquestionably assist you in improving your hearing.
The hearing aid contains some simple electronic components that are built-in that carry sounds from the environment in the ear and makes them louder or clearer for improved listening.
There are two primary categories of hearing aids. Both digital and analog hearing aids are powered by batteries. A tiny microphone that collects sound from the environment is installed in every hearing aid.
A digital code generator on an electronic circuit chip that amplifies and converts incoming sound. Noise reduction is the automatic sound reduction that occurs when sound is analyzed based on your hearing loss. Sound waves are sent to your ears via speakers when an amplifier converts one or more received sound waves or signals into sound waves.
1. Behind-The-Ear (BTE)
A behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aid lies behind the ear after hooking over the top. An ear mould, which is a bespoke earpiece that fits in your ear canal, is connected by a tube to the hearing aid. This kind is suitable for individuals of all ages and those with virtually any kind of hearing loss.
A hearing aid is worn behind the ear :
- The largest form of hearing aid historically, while some more recent micro variants are streamlined and scarcely perceptible
- Incorporates directional microphone is able to be amplified more than other types.
- May be more sensitive to wind noise than other kinds
- Conceivably be offered with a rechargeable battery
2. In-The-Ear (ITE)
One type of (ITE) in-the-ear hearing aid occupies the majority of the bowl-shaped section of your outer ear (full shell), while the other style fills only the lower portion (half shell). Both have directional microphones and are beneficial for those who have mild to severe hearing loss (two microphones for better hearing in noise).
An ear-worn hearing aid :
- It includes features such as a volume control that are incompatible with hearing aids of a smaller design.
- Possibly simpler to manage
- Uses a larger battery to increase battery life and offers a variety of rechargeable battery alternatives
- It is prone to having the speaker clogged with earwax
- May detect wind noise more intensely than smaller devices
- Compared to smaller gadgets, is easier to see in the ear
3. Receiver-In-The-Ear (RIE)
The speaker or receiver of the receiver-in-canal (RIC) and receiver-in-the-ear (RITE) designs is positioned in the ear canal, comparable to a hearing aid worn behind the ear. The component behind the ear is connected to the speaker or receiver by a small wire rather than tubing.
A hearing aid with a receiver-in-canal:
- Usually has a behind-the-ear section that is less noticeable.
- It incorporates directional microphones
- It has options for manual control
- Rechargeable batteries might be offered.
- It is prone to having the speaker clogged with earwax.
4. In-The-Canal (ITC)
A custom-molded hearing aid called an in-the-canal (ITC) hearing aid partially fits in the ear canal. Those with mild to moderate hearing loss may benefit from this approach.
A canal-mounted hearing aid :
- It is more covert than larger styles in the ear
- Has features that won’t fit on aids that fit entirely inside the canal, however, because of its small size, it could be challenging to adjust.
- It is prone to having the speaker clogged with earwax
5. CROS/BiCROS
Contralateral Routing of Signals is what the abbreviation stands for. Even though you can’t hear in one of your ears, a CROS system allows you to wear hearing aids in both of them. The aid on the “good ear” side receives the sound that the aid on the “poor ear” side has detected. The “head shadow” effect is eliminated as a result.
BiCROS hearing aids are extremely comparable to CROS hearing aids, with the exception that they are made for persons who also suffer hearing loss in their “good” ear.
The device in your better ear will be programmed with a BiCROS system to provide you with any necessary amplification. Bilateral is what the “Bi” stands for.
CROS and BiCROS work with batteries or are available as rechargeable hearing aids devices, similar to conventional hearing aids.
A hearing aid's price - How much do they cost?
All of our product lines have a variety of hearing aid designs, from custom models to covert behind-the-ear choices, to accommodate different degrees of hearing loss. The level of technology incorporated into our hearing aids determines their pricing, not necessarily their size.
Prices for hearing aids in India range from a reasonable basic range of Rs 20,000 to a premium of Rs 2, 50,000. If you want decent hearing aid pricing in India, you should first try, then decide based on how comfortable you are listening.
In Pune, prices for digital hearing aids range from 14,000 to 20,000. Visit Hearing aid plus Clinic if you want affordable hearing aids of various varieties in Pune that will help you select the suitable hearing aid.
Our Products

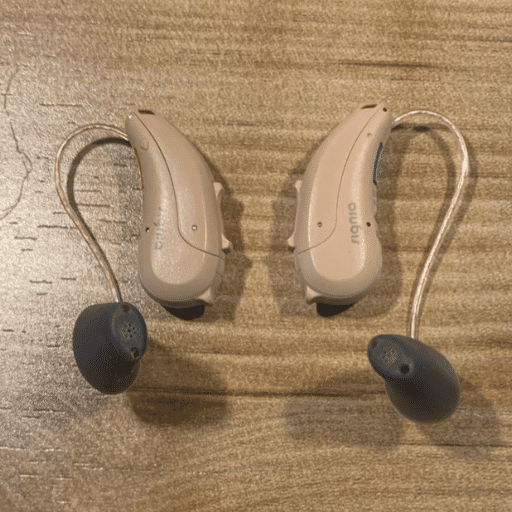
Behind-The-Ear hearing aid
Brand: Signia
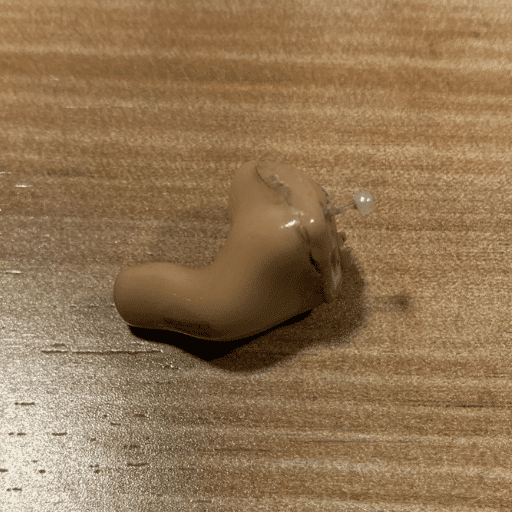

In-The-Canal (ITC) hearing aid
Brand: Signia

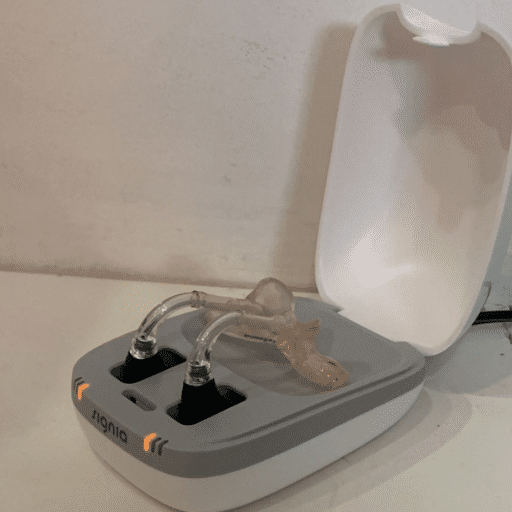
Receiver In-The-Ear hearing aid
Brand: Signia
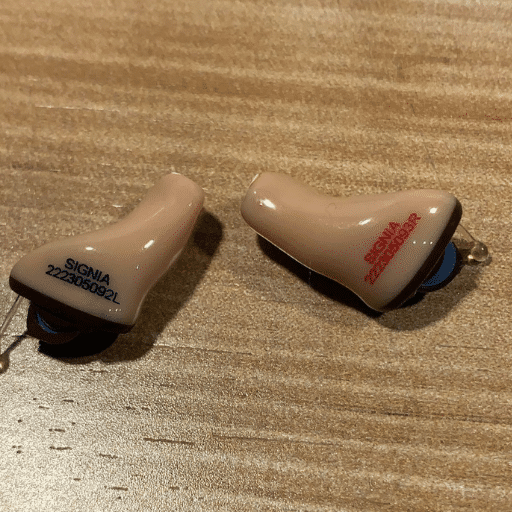

In-The-Ear (ITE) hearing aid
Brand: Signia
(CROS) hearing aid
Brand: Signia
FAQ regarding hearing aids and clinic
No! If you are using a proper digital hearing and programmable hearing aid suggested by your Audiologist or hearing care professional and programmed it properly will not increase your hearing loss by the aid. Except for other medical conditions.
A few types of hearing loss are heritable. Yet, not all hereditary types of hearing loss manifest at birth; others can develop later in life. For instance, otosclerosis, which is suspected to be a hereditary illness, impairs hearing later in life by preventing structures inside the ear from functioning properly due to abnormal growth of bone. Otosclerosis typically doesn’t cause hearing loss until a person is between the ages of 10 and 30.
You must examine several criteria while choosing a hearing aid to select the best model for you. Consider your lifestyle, your favorite pastimes, your employment, your eyesight, and your dexterity, as well as the type and extent of your hearing loss. Your options will also be influenced by the dimensions and contours of your inner and outer ear canals.
Typically lasting four to five years, and perhaps even longer, hearing aids are durable. Naturally, how well they are taken care of and how frequently they have worn both matters. You should conservatively expect your hearing aids to last five years. This is primarily due to the fact that hearing aid manufacturers are mandated to offer support for any discontinued hearing aid for at least five years after it is discontinued. You might have trouble finding replacement components for it if it breaks down after this time frame, and it will be deemed beyond repair.

